In this week’s Fourier Optics course we shall be looking at diffraction from 2D apertures, using Fourier methods.
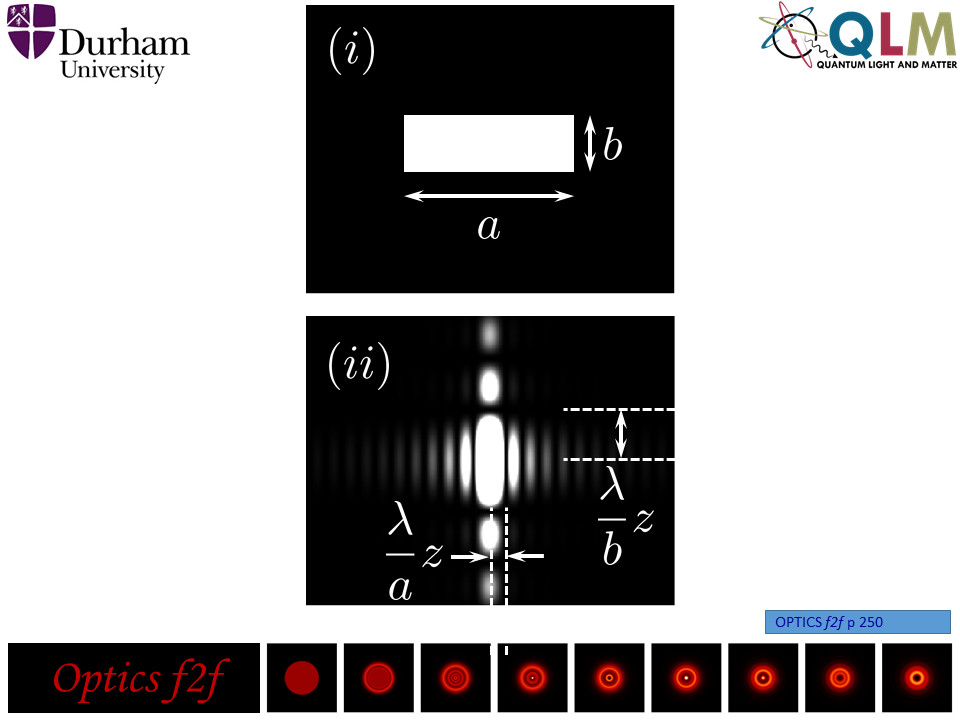
Here is a (Cartesian separable) rectangular aperture, and the corresponding Fraunhofer intensity pattern.
Here is a (Cartesian separable) rectangular aperture, and the corresponding Fraunhofer intensity pattern.
Comments
For example, here is diffraction pattern of E. Vertically we see interference of 3 identical copies of horizontal bars.
The simplest example is two circles. We see the Airy pattern modulated with cos-squared fringes – interference from the two apertures.
(i) Hexagonal shape of diffraction form one triangle
(ii) Vertical fringes with one subsidiary maximum between principal maxima
(iii) Horizontal fringes with one subsidiary maximum between principal maxima